[ad_1]
It’s really important that your business has a strong content marketing strategy. But just as importantly is the content delivery network (CDN) that underpins it. Without a good CDN, your content may load slowly, meaning prospects will bailout.
Confused?
Many online businesses haven’t yet got their heads around a content delivery network. And yet, as we shall see in this article, it can turbocharge your content marketing strategy so that more site visitors stick around – and convert.
Join us as we take a look at what a content delivery network is, why it’s important, and how it can boost your content marketing strategy.
What Is a Content Delivery Network?
A content delivery network is a variety of systems located around the world that deliver your web content as fast as possible.
To understand this in more depth, let’s take a look at the purpose of a CND, as well as how it works.
What Is The Purpose of a CDN?
A CDN is there to deliver your content securely and efficiently to visitors all around the world. It doesn’t matter where in the world a site visitor is located, a CDN aims to get the content to them as quickly as possible so that they (the end-user) have a good user experience. Whether a site visitor is located in Peru or Germany, a CDN is designed to deliver the content to each person at the same speed.
How does it do this? It does it by taking into consideration a user’s location. For example, let’s say an individual enters your site from their location, Peru. A CDN will then use the server that’s closest to them to allow your website to deliver your content as quickly as possible. On the other hand, if an individual accesses your website from Europe, the CDN will use a server that’s closest to them. Which, of course, will be a different server.
A CDN does more than this. See, there is more than just a location to take into consideration – there is also traffic. A CDN distributes traffic across multiple servers while at the same time boosting the overall performance of a website.
For instance, let’s say you’ve published a new blog post to your site and it suddenly goes viral. The viral nature of your content will cause a huge spike in traffic which will put your website under a massive amount of strain. Additionally, your server will suffer. Unless you’re using a CDN, your server might buckle under the pressure and go offline.
When you use a CDN, traffic is spread out over numerous servers. The clear benefit of this is that, even if an article goes viral, your website will stay online.
How a CDN Works
Each time an individual enters your website, a CDN uses the server that’s nearest to them to deliver and display the content as soon as possible. At the same time, that same server copies your cached files, including videos and images, as well as javascript files and HTML pages. It then stores them on hard-disk drives for safeguarding.
Why does it do this? It does it so that the next time an individual accesses your website from the same location as the previous person (or, at least, a nearby location), your CDN redirects the request from their server to the one that’s nearest to them. Thus, this nearby server is able to deliver the saved content in double-quick time!
Naturally, neither you nor the end-user notices any of this. A CDN works its “magic” behind the scenes, unseen and often unsung. All the end-user sees is whatever the page displays. But what they benefit from is the quicker loading time. Not just that, but they and you, the webmaster, benefit from safe and secure content.
As we can see, CDN relates to website performance. But it’s also worth pointing out – based on a guide at HostScore – that server performance is different to website performance. Server performance relates to how fast your server responds to requests, while website performance relates to the time it takes for your pages to load. Server performance does contribute to how quickly your pages load, but it’s only a part of what constitutes the overall performance of a website.
For example, things like additional plugins can slow down your website performance. But because server location plays a key role in website performance (and because it’s something many content marketers don’t take into consideration), a CDN is crucial.
Why a Content Delivery Network Is Important
Less Bounce Rate
User experience is super important to your conversions. If your website isn’t loading properly, users will bounce – and a high bounce rate is bad for SEO. It doesn’t matter how good your content is, users won’t engage with it if it isn’t loading properly.
A CDN Improves Site Speed
There are many reasons why users bounce (including a misleading title tag, the wrong page, a technical error, or a bad link), but site speed is perhaps the biggest. In fact, stats have shown that 37% of site visitors will bounce if a website takes longer than 5 seconds to load.
Site speed is not just bad for the user experience, it’s also bad for SEO. Google wants to provide the end-user with as much value as possible. If your website is taking too long to load, users will bounce and Google will assume that something is wrong with your site. Thus, it will drop you down the rankings. Where organic traffic is concerned, this is a really bad thing.
While a few things can cause slow site speed, using a CDN can give yours a shot in the arm.
A CDN Improves Site Security
More security is a key benefit of a CDN. A good CDN is able to prevent DDoS attacks from occurring, giving you (and your site visitors) a better piece of mind. It also gives you the option of enabling SSL.
And remember, when your customers know that your website is safe, their trust in you goes up. As a result, your reputation improves, as will your content marketing campaign.
Quicker Image Indexation
Image indexation can be a real pain in the butt because, the longer it takes Google to index your images, the worse off your SEO efforts will be.
Why is this?
Because images play a key role in both content marketing and SEO. By doing the “little” things, such as adding the right captions, keywords, and alt text to your images, as well as reducing file size, you can turbocharge your SEO efforts.
And when it comes to image indexation, using a CDN helps you to get it done quicker because – as we’ve already seen – using a CDN to serve your images (as opposed to your origin server) results in faster display time.
A CDN Means Your Content Is Always Online
As we mentioned earlier, good content can sometimes go viral. Whilst we all want this, the downside of viral content is spikes in traffic that can sometimes lead to downtime. And when you experience downtime, customer trust in you erodes, and your content marketing campaign suffers as a result. This is because users won’t hang around if your website takes too long to load, or doesn’t load at all. As mentioned before, research shows that 37% of site visitors will bounce if a web page takes longer than 5 seconds to load. And a high bounce rate can damage your SEO efforts by causing your page to drop down the rankings.
Because a CDN helps you avoid unexpected surges in traffic, the origin server is relieved of a massive load. As such, your website is always online and it’s a lot more scalable. As an added bonus, you won’t need to fork out extra money for a costlier hosting plan.
Potential Issues To Look Out For
As we’ve seen, there are plenty of benefits associated with a CDN. But if you don’t use yours correctly, you might fall foul of a few potential issues:
Potential Cross-Site Security Problems
If you run an SSL on your site but don’t enable it on your CDN, it could cause cross-site security issues. This happens because a Content Delivery Network uses encryption for the content they’re serving to a website that isn’t encrypted – but not the other way around. If your website is encrypted but you’re referring media that isn’t encrypted web visitors may be notified of any potential issues via a website browser warning. This alone could cause them to lose trust in your content. There’s also the chance that your website may not even load.
Potential Duplicate Content Problems
If you misconfigure your CDN, you may end up with duplicate content problems. This happens when different URLs are pointing to the same content. You can avoid this issue by using a rel canonical tag that uses an absolute path.
Note that, while this is extremely rare, duplicate content can cause Google to issue you a penalty. And if that happens, your content marketing and SEO efforts will suffer.
Potential Slow Loading Websites
While a CDN is meant to improve site speed, it may slow your website down if you’ve attached render-blocking media to it (the CDN). What happens is that the site visitor polls your web server as it looks to load the page. The page then begins to load but the site visitor must wait for the CDN to respond. For example, the text might load a second or so before a video. This creates a poor user experience. Fortunately, it can be avoided by proper implementation of the CDN.
CDNs To Try
CDNs can boost site speed and improve site security. It’s important, though, that you choose a good one that is relatively easy to set up and enable SSL. Here are some to check out:
Brandfolder
BrandFolder is a comprehensive digital asset management software that, among other things, acts as a CDN. It stores your digital assets, such as press releases, audio, videos, and logos, allowing you to manage and update them without any hassle.
And because it automatically tags your images and converts image copy into text, it helps users who are searching for specific assets.
Pros:
- Can be used for a wide range of tasks
- 24/7 customer support
Cons:
- Might be expensive for smaller teams
CMS Hub
One of the best things about CMS Hub is that you can also use it to host your website. It requires no setup and no configuration, and you won’t need to buy one from a third-party provider if it’s hosting your site.
CMS Hub guarantees fast site speed and decreases latency around the world for your site visitors.
Pros:
- 24/7 customer support
- Access to HubSpot
- Easy to set up for coders
Cons:
- Lack of a coder on your team might count against you
Amazon CloudFront

Like all good CDNs, Amazon CloudFront delivers your APIs, apps, videos, and data to your worldwide site visitors securely and quickly. Transfer speeds are high, latency is low, and – to add an extra layer of credibility – it’s the CDN used by Dow Jones, Hulu, and other enterprise corporations.
It’s also worth mentioning that you can pay-as-you-go with this CDN.
Pros:
- Reputable brand
- Pay-as-you-go payment model
- Free if you have less than 2,000,000 monthly requests
Cons:
- The pricing is dynamic but can also be high
CloudFlare CDN
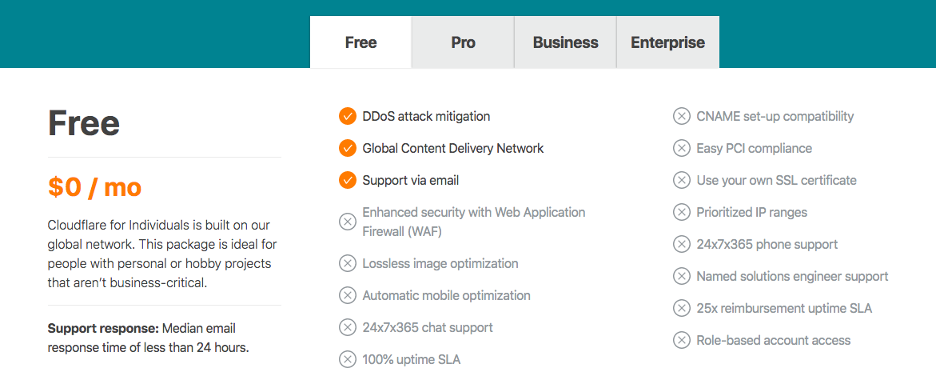
CloudFlare CDN houses a worldwide network of data centers located in over 90 countries and 200 cities. It also supports more than 25,000,000 internet properties and combines machine learning with data to send content requests with speed and reliability.
A free plan is available, while premium plans start at a rate of $20 a month.
Pros:
- Free plan available
- Inexpensive
- Easy setup
Cons:
- Not a CDN in the conventional sense
Conclusion
A CDN might represent the technical side of your content marketing strategy, but it doesn’t need to be complex. As long as you use the right CDN, you won’t even notice it. The best thing is that your site visitors won’t notice, either! Instead, they’ll be able to enjoy your awesome content hassle-free.
 Deana Kovač is an internet marketing specialist at Point Visible, a digital agency providing custom blogger outreach services. In her free time, she enjoys listening to music and singing karaoke. Also, her day just can’t start without a hot cup of coffee.
Deana Kovač is an internet marketing specialist at Point Visible, a digital agency providing custom blogger outreach services. In her free time, she enjoys listening to music and singing karaoke. Also, her day just can’t start without a hot cup of coffee.
Source link






